Battle of Words: Content Marketing vs Copywriting Compared
Master content marketing and copywriting for a captivating online presence.
Unleash the power of Features, Advantages, and Benefits (FAB) to write compelling content.
Have you ever felt like your marketing messages are falling flat?
You're not alone.
The problem is that many businesses and marketing teams focus too much
on features and not enough on benefits.
They list off all the bells and whistles of their product or service but don't explain why these features matter to the customer.
This is where the features, advantages, and benefits analysis (FAB) comes in.
The FAB-ulous Marketing formula is a simple but powerful marketing strategy that can help you create marketing messages that are more persuasive and effective.
Today, we'll break down the FAB formula and show you how to use it to create marketing messages that will help you achieve your business goals.
Imagine a product as a person.
A person has many features that make them unique, such as their height, hair color, and personality traits. Similarly, a product has many features that make it unique and valuable to users.
In simpler terms, a feature is an attribute that a product has or something it can do.
It's what makes a product useful and enables it to be of value to prospective users.
To illustrate this concept, let's consider some examples from popular brands:
A new product can have 5 different types of features to consider.
1. Functional Features: These features address the core purpose of the product and what it enables users to do. They focus on the practical aspects of the product and how it performs its intended tasks.
Examples include:
2. Design Features: These features encompass the aesthetic appeal, usability, and ergonomics of the product. They focus on how the product looks, feels, and interacts with users, making it aesthetically pleasing, easy to use, and comfortable to interact with.
Examples include:
3. Added-Value Features: These features go beyond the core functionality and provide additional benefits or enhancements to the product. They offer extra perks or capabilities that differentiate the product from its competitors and enhance its overall value proposition.
Examples include:
4. Quality Features: These features address the durability, reliability, and performance of the product. They ensure that the product is built to last, meets high standards of quality, and consistently delivers on its intended purpose.
Examples include:
5. Experience Features: These features focus on the overall user experience, encompassing the ease of use, intuitiveness, and emotional impact of interacting with the product. They strive to create a positive, engaging, and memorable experience for users.
Examples include:
Pro tip: To identify the features of your product, ask yourself,
What are the key characteristics that make your product or service unique?
What are the specific features that your target audience is most interested in?
Think of an advantage as something that gives a product a leg up, a special something that makes it more appealing or useful to users than its competitors.
To illustrate, let's revisit our examples from before:
In each of these examples, the advantages are what make the product more competitive and appealing to users, And that brings us to a new concept "Product Differentiation!"'
Product differentiation is a strategy that companies use to distinguish their products from those of their competitors. It involves creating a product that is perceived as being different or better than its competitors in a way that is meaningful to customers.
There are three main types of product differentiation:
Examples: Luxury vs. budget smartphones, high-end vs. affordable cars, premium vs. basic laptops
Examples: Smartphone brands with different operating systems (iOS vs. Android), cars with distinct designs (sporty vs. luxurious vs. family-friendly), computers with specialized features for gaming,
graphic design, or programming
Examples: Smartphones with premium features at a competitive price point, cars with luxury features and a mid-range price, and computers with specialized features for a specific target audience,
such as creative professionals or students.
Pro tip: To identify the advantages that are most important to your individual customers, ask yourself,
How does each feature benefit the customer? What makes each feature better than similar features of competing products or services?
In the context of products, a benefit is the positive outcome that a user gains from using a particular feature. It's the "why" behind the feature, the reason why a user would want to use it in the first place.
Benefits are closely related to advantages, but there's a subtle distinction. As you already know by now, An advantage is a quality that makes a product superior to its competitors, while a benefit is Why the customer will buy the product.
To illustrate,
Pro tip: To identify the Benefits of your product, ask yourself, What positive outcome will the customer experience as a result of using the product or service? How will the product or service improve the customer's life?
But, are all benefits the same?
The answer is NO! You have a wide category of benefits that you need to know:
Functional Benefits: Those are the practical advantages that a product provides.
They answer the question, "What does this product do for me?"
Examples of functional benefits include:
Social Benefits: They are the ways that a product helps you connect with others.
They answer the question, "How does this product help me feel connected to others?"
Examples of social benefits include:
Emotional Benefits: These are the ways that a product makes you feel.
They answer the question, "How does this product make me feel?"
Examples of emotional benefits include:
Epistemic Benefits: These are the ways that a product helps you learn and grow,
and satisfy a curiosity or a willingness to try something new.
They answer the question, "How does this product help me learn and understand the world?"
Examples of epistemic benefits include:
Aesthetic Benefits: These are the ways that a product appeals to your senses.
They answer the question, "How does this product look, sound, smell, taste, or feel?"
Examples of aesthetic benefits include:
Hedonic Benefits: These are the ways that a product gives you pleasure.
They answer the question, "How does this product make me feel good?"
Examples of hedonic benefits include:
Situational Benefits: These are the ways that a product meets your needs in a specific situation.
They answer the question, "How does this product help me in this particular situation?"
Examples of situational benefits include:
Holistic Benefits: These are the ways that a product improves your overall well-being.
They answer the question, "How does this product make my life better overall?"
Examples of holistic benefits include:
Now, why do you think we need to know the exact type of benefits of our product?
Good question!
Understanding the types of product benefits is like having a secret decoder ring for unlocking customer motivation. It's about knowing what makes your product tick and how it resonates with your target audience on a deeper level.
For example:
Just imagine you're selling a new fitness tracker. If you simply state that it tracks their steps, calories burned, and heart rate, you're only highlighting its functional benefits.
However, if you emphasize how it helps them achieve their fitness goals, feel more confident, and connect with a community of like-minded individuals, you're tapping into the social, emotional, and holistic benefits, making the product more appealing.
So to better understand the difference between features, advantages, and benefits, we can say that:
Features: What does this product have?
Advantages: Why is this product better?
Benefits: What will this product do for me?
Let's break it down:
Feature-driven marketing is like showing off your new Product. You're excited about your long feature list, and you want to make sure everyone knows about them. While this approach can be useful for technically savvy audiences, it's not always enough to convince someone to buy your product.
Benefit-driven marketing, on the other hand, is like showing someone how your product can make their life better. You're not just talking about the cool features; you're explaining how those features can solve a problem, make their life easier, or bring them joy.
So, which is better?
The answer is simple: benefits.
Why?
Because people don't care about features. They care about what those features can do for them.
When you focus on benefits, you're speaking directly to the heart of what your customers want.
You're showing them that you understand their needs, build an emotional connection with them,
and that you have a solution for them.
Advantage-driven marketing is a bit different. It's about showing how your product or service is the best one out there. You're highlighting your unique selling proposition (USP) and explaining why your product is better than the competition.
Advantage-driven marketing can be effective, but it's important to make sure you're not just bragging about yourself. You still need to focus on the benefits that your product or service's advantages offer.
So, when it comes to marketing products or services, focus on the benefits. Benefits are what will resonate with your customers and make them want to buy from you.
Here is a real example of benefits vs features vs Advantages of the Galaxy S23 page on Amazon
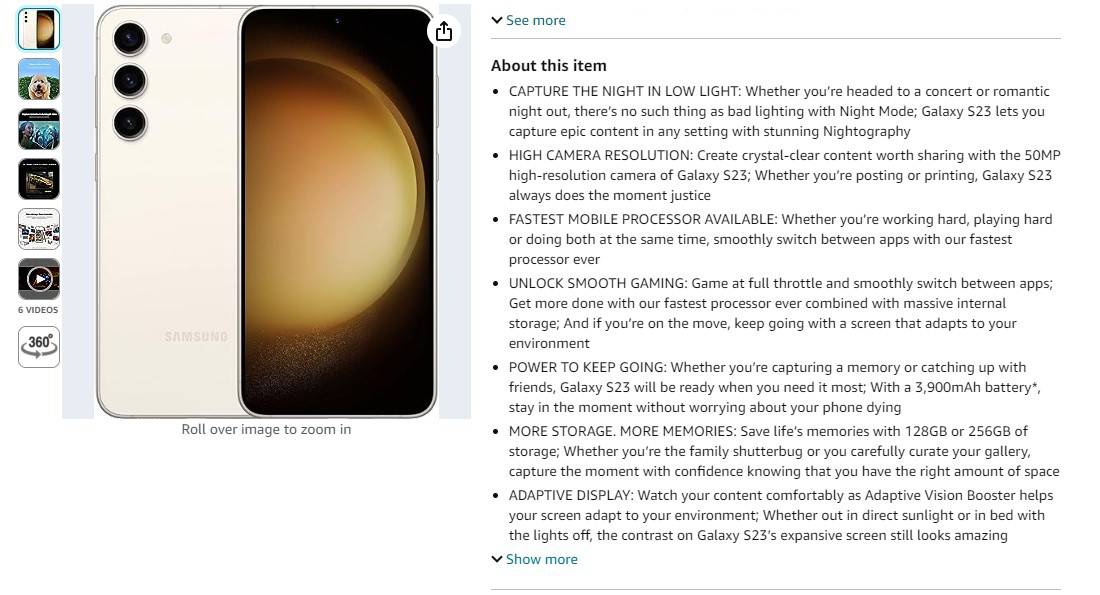
As you can see, the product description is very well-written and highlights the key features of the Galaxy S23 in a clear and concise way.
Here is a breakdown of the Features, advantages, and benefits analysis:
Feature: Galaxy S23's Night Mode, high-resolution camera, fastest processor, powerful battery,
and ample storage.
Advantage: Capture stunning photos and videos in low light, create crystal-clear content, switch between apps seamlessly, stay productive on the go, and save all your memories without worrying about storage space.
Benefit: Capture epic moments anytime, anywhere, enjoy a smooth and responsive experience,
stay connected and productive, and preserve your cherished memories.
Overall, the product description effectively communicates the value proposition of the Galaxy S23 and makes it an appealing choice for consumers.
The number of examples of FAB is enormous, especially on websites like Amazon, Walmart,
and Ikea as they always show you a list of features and why you might need them.
To summarize, it's crucial to keep in mind the wise words of the famous salesman Elmer Wheeler:
"Sell the sizzle, not the steak." This is a common marketing adage that emphasizes the importance of highlighting the benefits of your product or service, rather than just its features.
By doing so, you can maximize your marketing efforts by helping potential customers see the Importance
of what you offer for them.
Remember, In the sales process, people are more likely to buy something that they believe can enhance their lives, rather than something that merely exists to fulfill a basic need.
Master content marketing and copywriting for a captivating online presence.
Understanding your customer's awareness journey is pivotal to driving successful campaigns and achieving the desired goals.
Master content impact: Control angle, optimize effectiveness.
Be the first to know about new B2B SaaS Marketing insights to build or refine your marketing function with the tools and knowledge of today’s industry.